Environment
Tropical
Light
UVB
Temperature
85-115 °F
Humidity
80%
Most Active
Diurnal
Lifespan
15-20 years
Size:
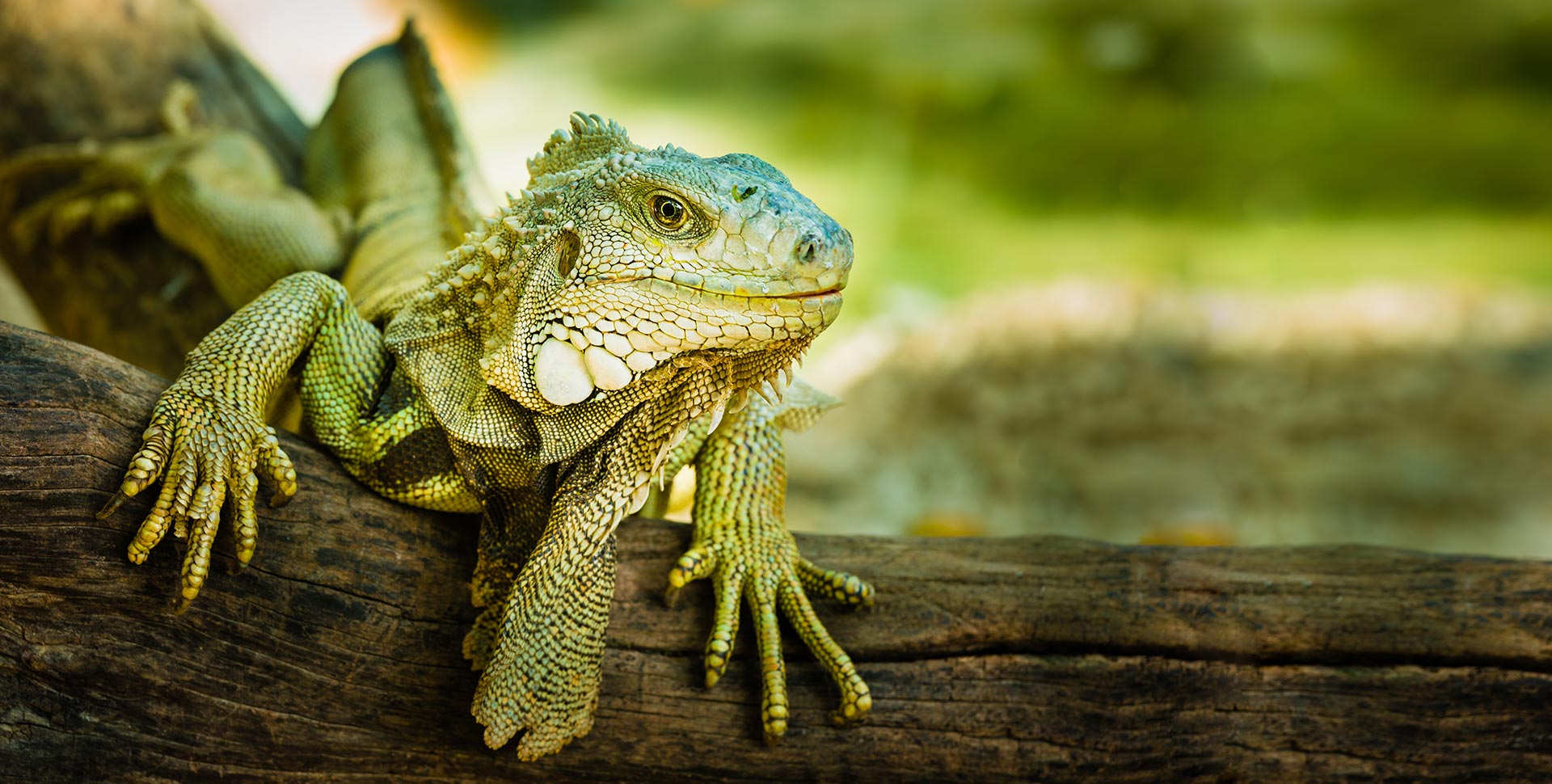
Green iguanas hatch out at approximately 2-4 inches from snout to vent and around 7-10 inches including the tail. Like many species of lizards, males tend to be larger than females. Including tails, adult males range from around 5-7 feet in size while females tend to average 4-5 feet.
Lifespan:
In captivity, with proper care, iguanas can live 15-20 years or more.
Enclosure:
When designing your Iguana’s enclosure make sure to remember that they are native to hot, humid regions with many options for climbing. Hatchlings can be kept in a 20 to 30-gallon tank for a short time. Adults need to have massive enclosures measuring 6 feet tall, 6 feet deep and 12 feet long. Outdoor enclosures are generally the best option for adults but indoor caging is fine when outside weather and temperatures will not allow a safe enclosure. It is possible to keep pairs or multiple females together but avoid multiple males as they can be territorial.
Temperature & Humidity
Providing a heat gradient with lows in the 80s and a basking spot of 100-115 degrees Fahrenheit is very important as reptiles are cold blooded and must be able to regulate their body temperature. Night temperatures can drop into the mid 70s and low 80s. A branch, rock, etc., should be placed about 5-6 inches under the heating element to ensure a proper basking spot and heat distribution.
Be sure to mist your Iguana’s cage 1-2 times a day or as needed to keep the proper humidity. Furthermore, Iguanas tend to prefer to drink water from their snouts that have been misted rather than a traditional water dish.
Humidity should be kept around 80 percent and increased during shedding. A great way to help control and maintain humidity during shedding and make your Green Iguana’s enclosure more natural is with mosses. Golden and Green Sphagnum Moss are all excellent at storing and maintaining humidity to ensure a clean, perfect shed if you live in a very dry climate.
Lighting
In addition to a basking spot, a full-spectrum UVB light is absolutely necessary. UVB lighting is essential in allowing iguanas to absorb calcium D3. There are many options for UVB and basking elements, consulting a breeder or knowledge pet store employee and research brands to determine the best options for your setup.
Feeding
Iguanas are herbivores and feed on a variety of grasses and vegetation in the wild. A high-fiber diet with supplemental calcium is recommended.There are many brands that create a captive diet specifically crafted to iguanas, consulting a breeder or knowledge pet store employee would be best for recommendations.
Dandelion greens, mustard greens, and hibiscus leaves are some popular supplemental foods that can be fed a couple times a week in addition to their normal captive diet.
Fruit can be given on rare occasions as they are high in sugars and should not account for more than 5 percent of the iguanas total diet. Some safe fruits are: strawberries, mangos, bananas, apples, tomatoes, grapes, apricots, and raspberries.
Water
Water dishes that are large are a great idea for Iguanas as it will allow them to soak and it will help maintain high levels of humidity. Adding a ramp is a good idea in case they slip or need extra help getting out after a good soak. Make sure to check water often as iguanas will occasionally defecate in their water dish. Hatchling and juvenile iguanas may have a hard time finding their water dish and must be misted multiple times a day and soaked a couple times of week to make sure they are hydrated.
Substrate
Iguanas do well on a variety of different substrates. Cypress Mulch, Orchid/Fir Bark, and Coco Husk are great naturalistic substrate options that help maintain and control humidity. There are also several types of soil mixes but Bioactive, ABG mixes, and Coconut Soil mixed with Golden Sphagnum Moss are some of the most common. These mixes are also great naturalistic substrate options that help maintain and control humidity. Adding on Leaf Litter is another great idea as it provides shelter, humidity, and is ideal for microfauna when doing a naturalistic enclosure. No matter what substrate you decide to use make sure to keep an eye on humidity as too much or too little can cause problems.
Hides
Providing a safe hiding place for your iguana is extremely important to the overall health of your reptile. Green Iguanas need a secure, dark cave or hide that they can retreat to in order to reduce stress and feel safe. It is best to have two hides in the enclosure with one placed on the hot side and one on the cold side. This is so the iguana can properly control its temperature and feel safe no matter which side they choose.
There are a variety of hides and foliage available on the market that can be used to accomplish these secure hiding places. However, when the Iguana starts to reach 3-4 feet many keepers have to craft their own hides as there are none commercially available to house that large of a lizard.
Decor
Green Iguana enclosures need to have a good amount of climbing decor. Spider Wood, Manzanita, and Driftwood are popular climbing implements that provide a different texture and aid in shedding. Natural Stones and Mosses are also a great addition for general stimulation and enrichment with the added benefit of a naturalistic enclosure.
Interesting Facts:
- Green Iguanas are considered an invasive species in many areas and are known as gillina de palo, meaning “bamboo chicken” or “chicken of the trees”. In the United States, there is a large feral population that exists in South Florida, Hawaii, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
- Like many other reptiles, iguanas have a small, photosensitive spot between their eyes. This is referred to as a “primal eye” and is thought to help reptiles thermoregulate their bodies by sensing the difference in various lights to help assist them in choosing the best place to bask.
- Iguana iguana is considered one of the largest species belonging to the genus Iguana.
- Despite their name, Green Iguanas can come in a variety of colors including: blue, black, lavender, teal, and even a reddish brown.
There are some differences in physical appearances of green iguanas as there used to be two different subspecies of Iguana iguana that developed in different geographical regions. I. i. Iguana developed in South America while I. i. rhinolopha was found in Central America. However, they are no longer separate and both belong to Iguana iguana.